What is Bitcoin?
Bitcoin is a deflationary digital currency that operates on a peer-to-peer network without the need for intermediaries. Introduced to the world in 2009 by an anonymous entity known as Satoshi Nakamoto, Bitcoin aimed to revolutionize the financial landscape by offering a secure, borderless, and permissionless peer-to-peer system for conducting transactions.
Key Characteristics of Bitcoin
-
Scarcity: Currently, there are 19.8 million Bitcoins in circulation. According to the design, the total supply will never exceed 21 million. There are 1,198,000 Bitcoins left to be mined, and it's projected that by around the year 2140, the last Bitcoin will be mined. The issuance of these remaining Bitcoins occurs through an energy-intensive process, with the mining reward halving approximately every four years.
-
Decentralization: Bitcoin operates on a decentralized network of computers, known as nodes, ensuring no single entity has control over the currency, nor is it able to change the rules that govern the Bitcoin network.
-
Permissionless: Bitcoin allows individuals to transact directly with one another without the need for intermediaries like banks or payment processors. This enables secure, borderless, and censorship-resistant transactions with minimal fees, no need for currency conversion, and above all, monetary freedom.
-
Pseudonymous: Bitcoin transactions are pseudonymous, represented by unique alphanumeric addresses rather than real-world identities. While transactions are visible on the public blockchain, the identities of the parties involved remain anonymous unless voluntarily disclosed.
-
Trustless: Unlike other store of value assets such as gold, art, and the luxury sector, Bitcoin can't be counterfeited; its authenticity can be verified by anyone without expensive equipment or expertise.
How Bitcoin Works
Crypto guides will often refer to Bitcoin as a digital asset or decentralized token. At the core of Bitcoin is blockchain technology, a distributed ledger that records all transactions across the network. Transactions are verified through a process called mining, where powerful computers compete to solve complex mathematical puzzles. Once a puzzle is solved, the transaction is confirmed and added to a block, forming a chronological chain known as the blockchain.
The Bitcoin blockchain started in 2009 from zero, with the first 50 Bitcoins mined in the Genesis Block or Block Zero. Initially, 50 Bitcoins were printed into existence every 10 minutes, but this mining reward is halved approximately every four years to control supply inflation. The next halving is expected to occur in 2028 when the block reward will fall to 1.625 BTC.
Bitcoin mining is not about Mathematical Puzzles
Contrary to popular belief, Bitcoin mining isn't solely about solving complex mathematical problems. Here's a breakdown of the actual process:
-
Step 1 - A user sends a transaction from his wallet with a specified amount and receiving address.
-
Step 2 - The transaction is broadcasted to Bitcoin nodes, which verify its validity and add it to the mempool, a temporary storage area for unconfirmed transactions.
-
Step 3 - Miners aggregate and monitor mempools to select the most lucrative transactions to include in the new block: The transactions selected are typically smaller ones, as more of them can be included in the block, each providing its own transaction fee; however, larger transactions can also be prioritized when these pay higher fees.
-
Step 4 - Block creation: This involves organizing the selected transactions into a block structure along with other necessary data, such as the previous block's hash, a timestamp, and a nonce (number that is only used once). All this information is then transformed into a string of characters and numbers through a SHA-256 cryptographic hash function.
*A function is code that takes an input and in essence transforms it to generate an output, which (in this case) can’t be traced back to the original input.In this context, miners hash the block header and transactions, think of it as putting a selection of ingredients into a blender making it impossible to determine what were the original ingredients from the resulting liquid:
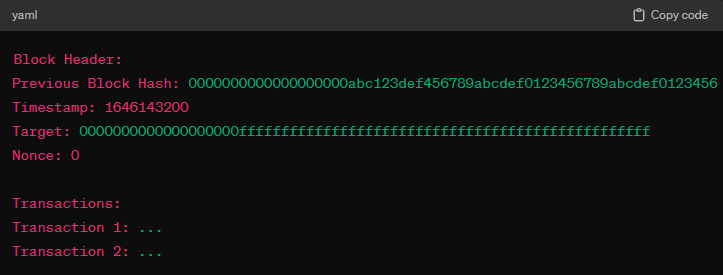
All of the info above is hashed (or blended if you want) into a string of 256 bits (zeros and ones), which due to its length is expressed in 64 hexadecimal characters like this example:
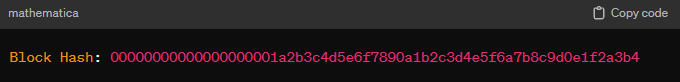
In order for a miner to win the block, the resulting Hash must be lower or equal to the Difficulty Target number, which is done by simply changing the nonce number at every attempt, which in turn modifies a small part of the resulting hash.
-
Step 5. Announcing the winning hash and peer validation
Once a miner discovers a nonce that produces a hash within the target difficulty, they announce their success to the rest of the network. Other nodes can quickly verify the validity of the new block by independently hashing the block's data with the announced nonce and confirming that the resulting hash meets the target difficulty.
-
Step 6. A new block, coinbase and transaction fee distribution
If the new block is deemed valid by the majority of nodes on the network, it is added to the blockchain, and the transactions it contains are considered confirmed. The miner who successfully mined the block is rewarded with a predetermined number of newly minted bitcoins (also known as coinbase, and yes, there’s an exchange named after it) that are unspendable for the first 100 confirmations (or blocks), as well as any transaction fees associated with the transactions included in the block, which are immediately available.
Why will Bitcoin succeed
-
Reason 1: Debt Spiral, Modern Monetary Theory & Deficit Spending
For decades, deficit spending has been the bread and butter of most countries. Many of the leading economies carry a high level of debt ranging from 60% to almost 300% of their own GDP. Since these debts must be repaid to prevent a financial crisis, countries like the US allocate a significant portion of their revenue to paying off debt interest (20% of their total revenue or 40% of personal income tax revenue). The problem arises from the perpetual cycle of spending more than we have, acquiring new loans to repay the interest on previous loans, leading to a continuous increase in interest payments. The equation is straightforward:
Less revenue = More deficit = More loans = More debt = More interest payment = Less revenue
The sensible solution would be to reduce government spending below revenue and begin repaying the principal debt, if we could turn back time a few decades. The alternative, less elegant solution, is to continue inflating the money supply by issuing more currency, which increases the value of financial assets and/or reduces purchasing power.
Recognizing the inevitable debt spiral, some individuals and institutions worldwide are acquiring bitcoin, precious metals, art, luxury items, and vehicles to safeguard and preserve the value accumulated over the years.
-
Reason 2: Broken Money
The last two decades provide undeniable evidence that the current monetary system is flawed. Countries like Venezuela had their gold reserves seized, while Russia, Iran, and Afghanistan faced similar issues with their foreign reserves. Although these countries are notorious dictatorships, the fundamental point is clear: a country's money is at risk if it falls out of favor with major powers like the US or the EU. Foreign reserves become a significant liability for a country's sovereignty, as the issuing country can easily freeze or seize them.
Given this trend of states seizing assets, it's reasonable to question the safety of citizens' money. Cyprus's seizure of 6-10% of accounts larger than 100k EUR in 2013, the US's Operation Choke point pressuring financial institutions, and Canada freezing bank accounts of anti-vaxxer protestors illustrate this vulnerability.
-
Reason 3: Sovereign Individual and freedom
Bitcoin empowers the sovereignty of the individual by enabling people to transact with anyone around the world, without requiring permissions, and essentially allowing them to relocate freely. Imagine a country experiencing war, invasion, civil unrest, or a change in political regime with significant tax increases. It's easier to cross a border with 12 written or memorized words than with precious metals or fiat currency, let alone with a real estate title that may become worthless or need to be sold at a fraction of its value.
-
Reason 4: Programmed Scarcity
Bitcoin has a current supply of 19.8 million BTC per year, inflating its supply by the creation of 900 BTC per day, roughly equating to a 1.6% supply inflation per year. This rate will decrease to 0.84% after the halving in April 2025.
Gold has a slightly lower inflation rate estimated between 1-2%, depending on various factors.
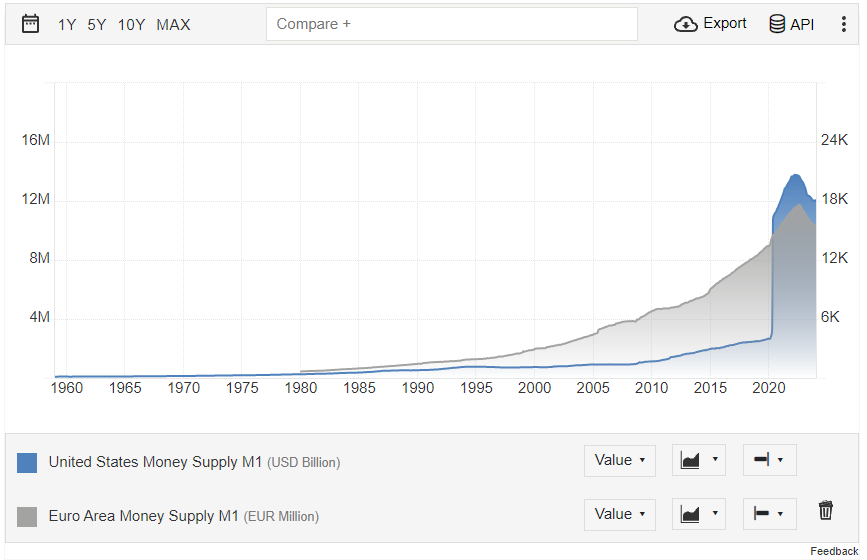
On the other hand, fiat currency continues to expand whenever the government spends more than its revenue, resulting in increased debt. The graphic below illustrates the M1 money supply for the Euro Area and the US dollar, which has been growing rapidly, driving asset prices higher as citizens seek refuge in harder assets. Although the first half of the graphic may appear relatively flat, it is distorted by massive money creation for Covid relief. Unlike other assets, fiat money is not constrained by the difficulty of production; it is created (or devalued through inflation) to address various governmental needs such as wars, foreign aid, subsidies, and projects that citizens may not have a say in.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Are Bitcoin Transactions Anonymous?
Many of you have likely searched for information about anonymous crypto exchanges, or the anonymity of crypto transactions. This Bitcoin guide aims to provide detailed insights into anonymous exchanges, the best crypto mixers, as well as the best crypto wallet options.
It is important to understand that while some platforms may offer anonymity, it largely depends on whether you provide personal information through KYC (Know Your Customer) forms or sign up with your personal email. Additionally the usage of VPN will prevent these platforms from recording your IP address, which will further preserve your anonymity.
In reality, Bitcoin transactions are recorded on a public ledger accessible to everyone. To maintain anonymity, it's crucial to avoid common mistakes or oversights that will disclose your identity and forever link that address to you:
Giving up your identity: Exchanges, addresses & internet safety
Individuals typically disclose their identity by purchasing Bitcoin through a centralized exchange that requires identity verification, a payment method tied to your identity (such as a credit/debit card or bank transfer), and a withdrawal address. If requested by a government institution, the bank will disclose your transactions with the exchange, and the exchange will reveal what you purchased and where you sent it.
Address reusability
Another way individuals compromise their anonymity is by reusing addresses. Once one of your addresses is linked to your identity, other addresses you transact with can be scrutinized, leading to an inference of a relationship with your identity.
Internet Privacy
While a direct link between a wallet address and your identity may not be established, your Internet Service Provider (ISP) can easily track the cryptocurrency-related sites or exchanges you connect to, inferring an interest in cryptocurrencies and potentially issuing information requests to these sites.
How to Buy Bitcoin Anonymously?
For those seeking anonymity or simply privacy, one of the most effective methods is utilizing anonymous crypto exchanges and funding purchases with gift cards or prepaid cards. To ensure maximum privacy, it's crucial to use cash when purchasing these cards in-store.
Anonymous Crypto Exchanges
Anonymous exchanges, often mistaken with decentralized exchanges, allow you to purchase cryptocurrencies without submitting KYC information. The main difference lies upon the funding options, decentralized exchanges only accept other cryptocurrencies as a funding option but anonymous exchanges also accept more commonly used traditional, yet unconventional, funding options.
-
Paxful P2P exchange
Paxful is one of the best sites for peer-to-peer buying and selling of cryptocurrencies, offering various payment options such as traditional methods, prepaid cards, gift cards, game items, and remittance companies.
It’s advisable to browse the offers and prices first to determine which particular brand gift card you will use. Buy it with cash in a store and keep the receipt in case the seller requests it. Once you are ready to execute a trade, the cryptocurrency side goes through Paxful's escrow service to provide an extra layer of security and ensure a smooth transaction.
Another alternative, potentially more cost-efficient, is Bitcoin stores and ATMs. You can simply search for them online or visit CoinATMradar for a quick overview of pricing and conditions. Most of these outlets allow you to buy up to 999 USD/EUR worth of crypto, but larger transactions may require documentation.
It is essential for prospective buyers and sellers to research pricing and conditions beforehand because Bitcoin stores and peer-to-peer exchanges often deviate significantly from the spot price advertised by most centralized exchanges.
Here’s our crypto blog’s detailed review of the best crypto exchanges available.
Safest Crypto Exchange
For those prioritizing convenience over privacy, reputable cryptocurrency exchanges provide added security, bigger rewards and overall a better pricing. That is not to say they are without risks, you have probably heard of FTX crypto exchange or Celsius crypto lending platform going into bankruptcy because they were taking massive risks with users' funds. In this context, it is crucial to understand that, exchanges of any kind, are nothing but a temporary storage for cryptocurrencies that are meant to be traded; these are no places to store your crypto as they are not in your control. Now, let’s have a look into the safest exchange with the lowest fees available:
-
Coinbase is one of the oldest and most reputable exchanges in the space. This publicly traded platform (Nasdaq: COIN) offers access to hundreds of cryptocurrencies, relatively low spreads, and much better withdrawal fees to your private wallet. Furthermore Coinbase offers a learn and earn incentive program to earn free crypto for learning about the various coins they list.
Here’s our cryptocurrency blog’s detailed review on the best exchanges available.
How to Choose a Wallet
Choosing a wallet depends on the cryptocurrencies you plan to hold, the frequency at which you plan to access it and the connectivity you require. Assuming you intend to acquire more than a few hundred dollars worth of Bitcoin, it is advisable to invest in security by acquiring a hardware wallet for long term holding, such as a Bloskstream Green or a Ledger.
If not, a desktop or mobile wallet is also a good choice, specifically the Samourai wallet which includes Tor routing and Coinjoin (mixing) features. Finally, for the ones seeking higher connectivity with smart contracts and NFT’s, Methamask or Phantom wallet are great browser extension wallets depending on the blockchain you focus on.
Here’s our cryptocurrency blog’s detailed review on the best software and hardware wallets available.
Based on our experience, we analyze below the nest practices in selecting a crypto wallet:
Privacy
Preserving your pseudonymity is achievable as long as you avoid establishing a direct link. The first step is to obtain a VPN subscription without using a payment method tied to you, such as Bitcoin or a prepaid debit card purchased with cash. While your Internet Service Provider (ISP) knows your identity and location, as they installed your service, the aim is to prevent your ISP from tracking the sites you visit by introducing a VPN intermediary. The VPN provider won’t know your identity but will still be able to see the sites you connect to.
Finding the top VPN for crypto exchanges can be a challenging task for some players. Thankfully, we’ve created a detailed crypto guide with the best VPN for crypto exchanges.
Additionally, for an added layer of security, you can use the Tor Browser. It functions similarly to a VPN, but with the distinction that the data is encrypted and relayed through three random servers instead of a single one as with a VPN.
Address Hygiene
As mentioned earlier, Bitcoin operates on a publicly available decentralized layer, allowing anyone to track the amount of bitcoin in a specific address. When transacting with Bitcoin, it typically involves disclosing one of your Bitcoin addresses to your counterparty. Therefore, it is advisable to practice address hygiene to avoid creating links between your addresses. This includes refraining from consolidating positions and creating new addresses when necessary. For instance, if a stranger wishes to gift you $50 worth of BTC, it would be imprudent to use an address where you hold most of your holdings, as this would reveal your total Bitcoin balance. The same precaution applies when dealing with exchanges or any entity that has knowledge of your identity.
Mixing coins for privacy
-
What is a crypto mixer?
A crypto mixer or tumbler service is a tool used to enhance the privacy and anonymity of cryptocurrency transactions. It essentially works by compiling multiple inputs from various users and shuffling them to break the link with their original addresses.Some anonymous crypto, like Monero do not require mixing services because neither the transaction nor the wallet balances are public.
Here’s our cryptocurrency blog’s detailed review on the best Crypto Mixers or you can read about Coinjoin (Bitcoin-only) mixing service below:
-
Coinjoin: Bitcoin mixing
CoinJoin works by combining multiple Bitcoin inputs from various users into a single transaction, making it challenging for outside observers to determine which input corresponds to which output. This process breaks the traceability of transactions, enhancing privacy for participants, and maintaining the fungibility of Bitcoin.
Here's how it typically works:
-
Transaction Mixing: Users who want to increase their privacy initiate a CoinJoin transaction. Each participant submits their inputs (unspent transaction outputs) and desired outputs (addresses they want to send funds to) to the CoinJoin transaction.
-
Combining Transactions: The CoinJoin protocol combines these inputs and outputs from multiple participants into a single transaction. This process effectively "mixes" the inputs and outputs, obscuring the connection between them.
-
Equal Output Sizes: To further enhance privacy, CoinJoin transactions often ensure that all outputs have the same size. This makes it more difficult for outside observers to link specific inputs to specific outputs, as there are no distinguishing features in the transaction outputs.
-
Transaction Broadcasting: Once the CoinJoin transaction is constructed, it is broadcast to the network and confirmed like any other transaction. Since the inputs and outputs are mixed, it becomes significantly more challenging for third parties to trace the flow of funds. Additionally CoinJoin offers a unique advantage known as UTXO consolidation, which can lead to reduced transaction fees over time. When users participate in a CoinJoin transaction, their unspent transaction outputs (UTXOs) are combined with those of other participants, resulting in fewer individual UTXOs. This consolidation optimizes the use of blockchain space and can result in smaller transaction sizes and lower fees. As a result, over time, users who regularly engage in CoinJoin transactions may experience cost savings on transaction fees compared to those who do not.
Here’s a short tutorial on how to Coinjoin through one of the most anonymous crypto wallets, the Samourai’s wallet Whirlpool.
Time locking Bitcoin
There are several reasons why you might choose to voluntarily lock your Bitcoin. Whether you aim to prevent impulsive spending or prioritize security concerns to safeguard against potential coercion, time locking offers a solution.
Time locking functions by transferring Bitcoin to either your existing wallet or a new one, effectively making the BTC unspendable for a predetermined duration. This process mirrors the concept of bank vaults, which can only be accessed at specified times. The duration of the timelock can vary from a few minutes, suitable for immediate needs like texting, to several years for long-term storage and capital appreciation strategies.
It's crucial to practice with small amounts initially, ensuring familiarity with the process. Incorrect input values in the transaction could potentially lock your BTC for thousands of years.
Here's a brief guide on how to implement it: Time lock Bitcoin.
Do you have to Pay Taxes on Crypto ?
This cryptocurrency blog cannot provide individual fiscal advice but it can tell you about the basics of it and the advantages of being a resident in a particular country.
In most countries, you're required to declare your crypto gains as income tax, just like other financial assets. Some countries however have provided incentives or exemptions provided some conditions are met. Germany, for example, doesn’t require citizens to pay income tax on Bitcoin profits as long as the asset has been held for over a year. El Salvador, where Bitcoin is legal tender does not require taxes on Bitcoin since they declared it actual money. The best advice we can give is to keep a clear record of the purchasing and selling price, consult with a fiscal advisor or relocate to the safest country in the American continent.
Do you have to report crypto on taxes if you don’t sell ?
If you don't sell your holdings, most countries won't be required to pay taxes. Nevertheless, it's essential to include your crypto holdings in your personal wealth declaration, which is typically mandatory once you exceed a certain threshold. For instance, in Switzerland, although crypto gains aren't taxed directly, there's a 0.3% wealth tax that encompasses crypto holdings.
Wealth tax thresholds vary, typically starting around $600,000 to $800,000, depending on the country. Citizens are required to declare and pay taxes based on the unrealized market value of their assets.
Here's a brief overview of what taxes look like in various countries: Crypto Taxes.
How to Spend Bitcoin on Online Purchases
Contrary to misconceptions held by some no-coiners, Bitcoin is not solely limited to speculative investments or trading for other cryptocurrencies. In fact, there is a growing number of businesses across various industries that accept Bitcoin as a form of payment.
Platforms such as Bitrefil and Bitpay serve as great resources for individuals seeking to use their Bitcoin holdings for online purchases. These platforms offer a diverse array of brands spanning leisure, travel, fashion, technology, restaurants, and more, all willing to accept Bitcoin in exchange for their goods and services.
Additionally, once you have figured out what brand you will be buying from, you can go back to the Peer to Peer exchange and trade your Bitcoin for a significantly higher price in the form of gift cards of that specific brand.
How to Earn Bitcoin for Free
No, it’s no clickbait, you can actually earn cryptocurrencies without spending any money. Even now, you can still earn a few hundred dollars by 2 particular ways:
Learn and Earn
Exchanges and similar centralized platforms will credit you anywhere from 1 to 10 USD for taking quick short minute lessons on a particular topic and correctly answering a quiz. The money comes from marketing efforts from the project itself and or the exchange to build up loyalty or increase active use of the platform.
Advertising
Faucets, micro tasking sites and earn free crypto apps will pay you for your active use of their platform or app. They do so because they monetize your time on the app through advertisements of legitimate brands and the large majority advertising fraudulent products or services. You can read this cryptocurrency blog for more ways to earn free crypto, options include signing up bonuses, move to earn apps, faucets, Learn and Earn, staking & lending, cashback cards and referrals.























































